Neuracle Science Technology
NS101
| Pipeline | NS101 |
|---|---|
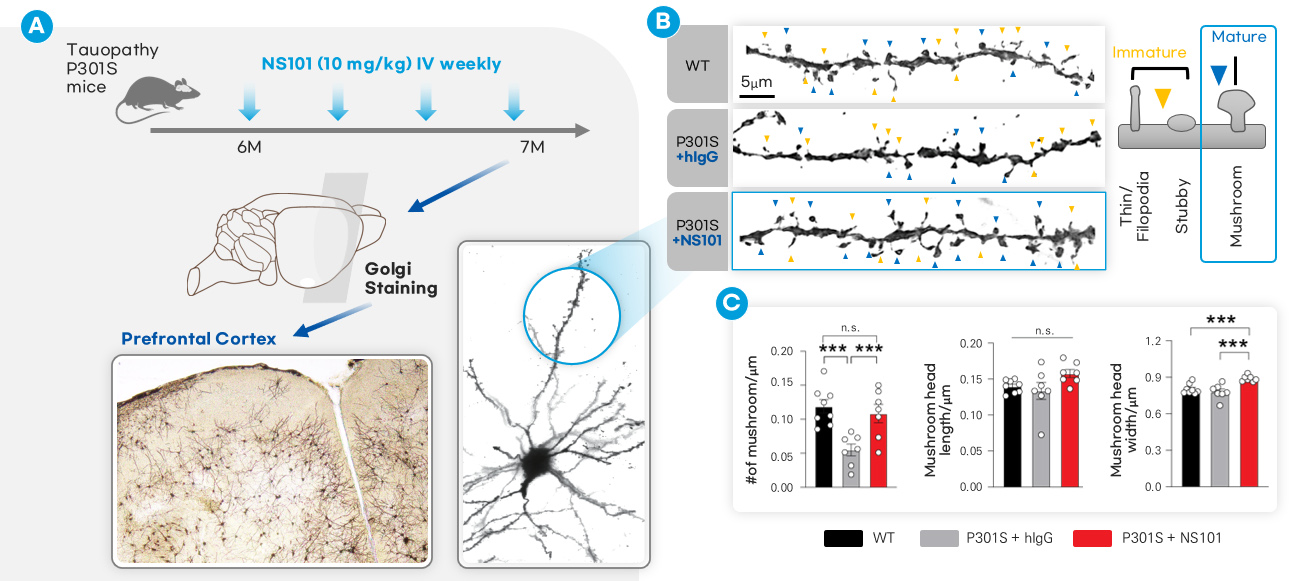
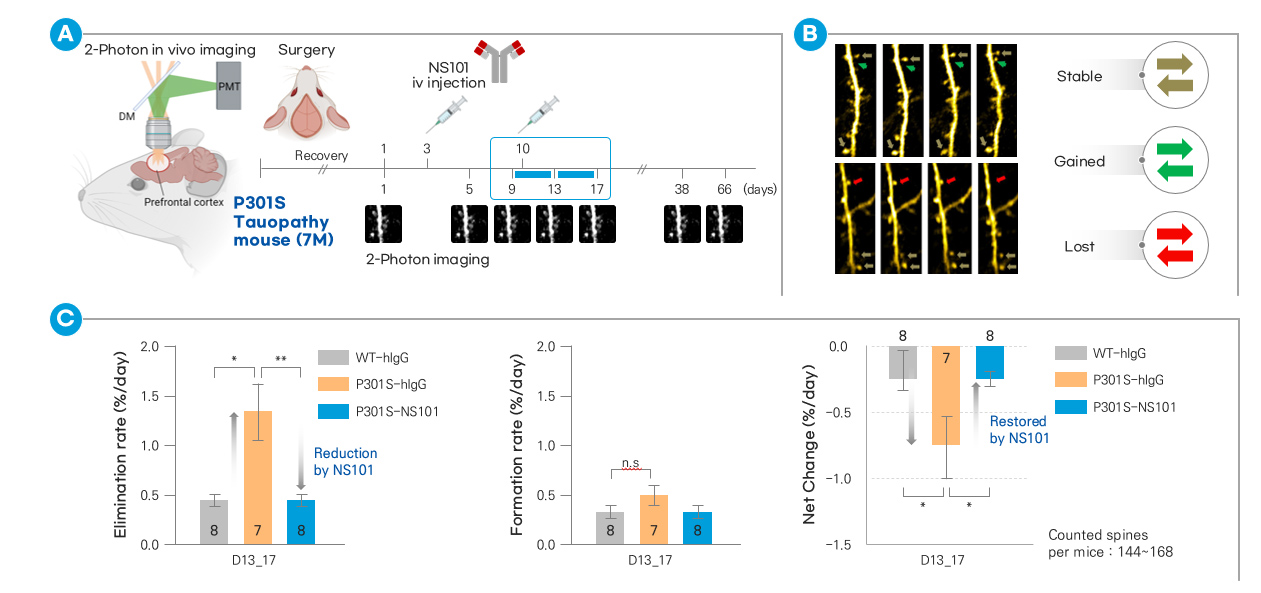
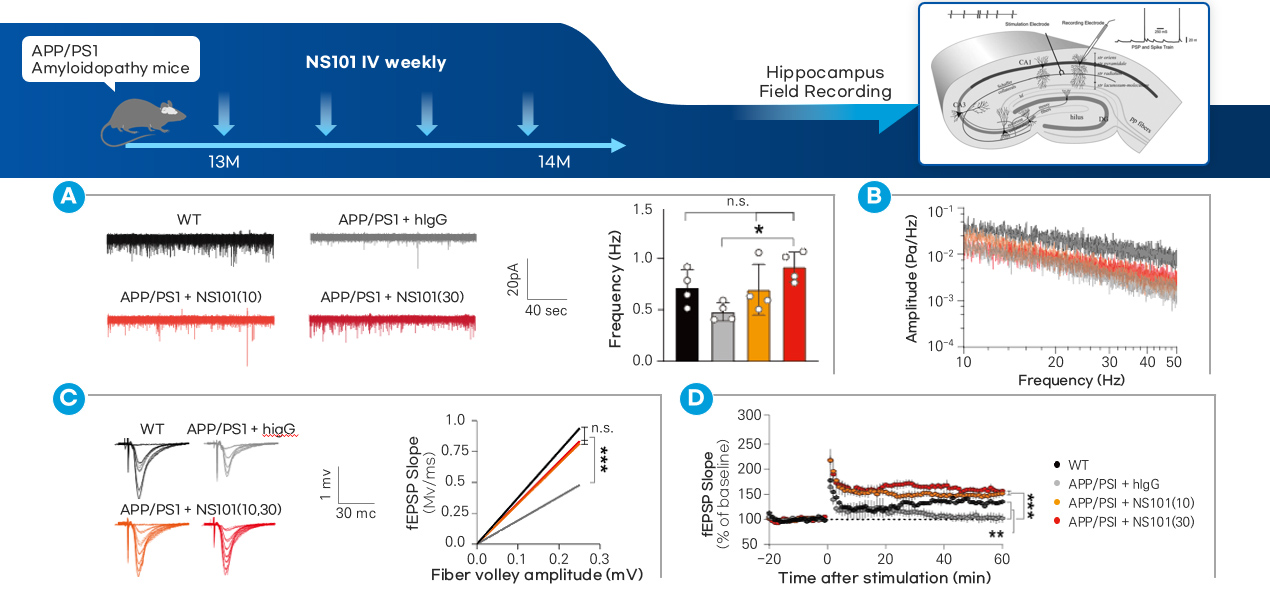
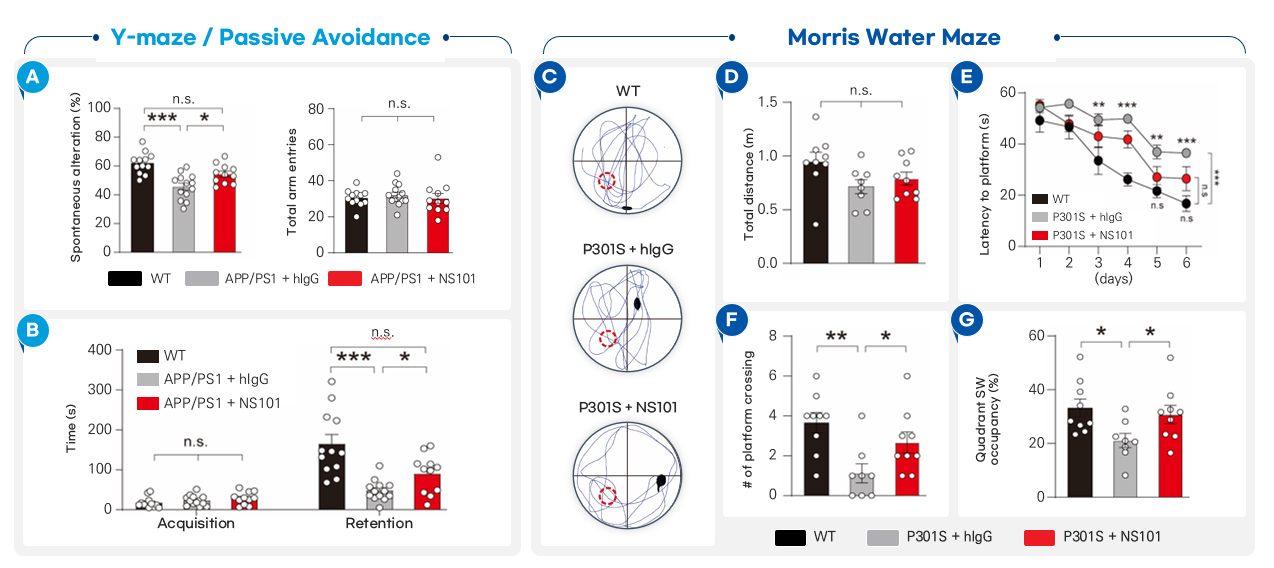
| Summary | NS101 is a monoclonal antibody drug candidate that promotes the reconnection of damaged synapses, by neutralizing the FAM19A5 protein which inhibits synapse formation. |
| FAM19A5 | Information transmission in nerves occurs through organelles called synapses. Synapses in nerves are formed by the adhesion of presynapses and postsynapses. A synaptic adhesion protein called PTPRF is present at the presynapse of a nerve cell axon. A synaptic adhesion protein called LRRC4B is present at the postsynapse of neuronal dendrites. The role of FAM19A5 is to bind to LRRC4B at the postsynapse and inhibit synaptic connections, by interfering with the formation of the synaptic adhesion complex of PTPRF and LRRC4B. This inhibitory function of FAM19A5 contributes to disruption of the repair and regeneration of damaged neuronal synapses. Thus, FAM19A5 interferes with the neuronal recovey in a variety of disease conditions, including Alzheimer's disease, hearing loss, optic nerve disorders, traumatic brain injury, and spinal cord injury. |
| NS101 |
NS101 is a monoclonal antibody that binds to FAM19A5, and promotes synaptic reconnection by disinhibiting FAM19A5-mediated inhibition of synaptic adhesion. The efficacy of NS101 will be applicable to a variety of neurological diseases with structural and functional impairment of synapses (synaptopathy) as a primary pathogenesis, including sensorineural hearing loss and Alzheimer's disease. |
Structure and pharmacology
Alzheimer's Disease - Nonclinical
Sensorineural Hearing Loss - Nonclinical
NS101 administration inhibits noise-induced loss of Ribbon Synapses in mouse inner ear cochlea, which in turn inhibits the noise-induced loss of hearing function.
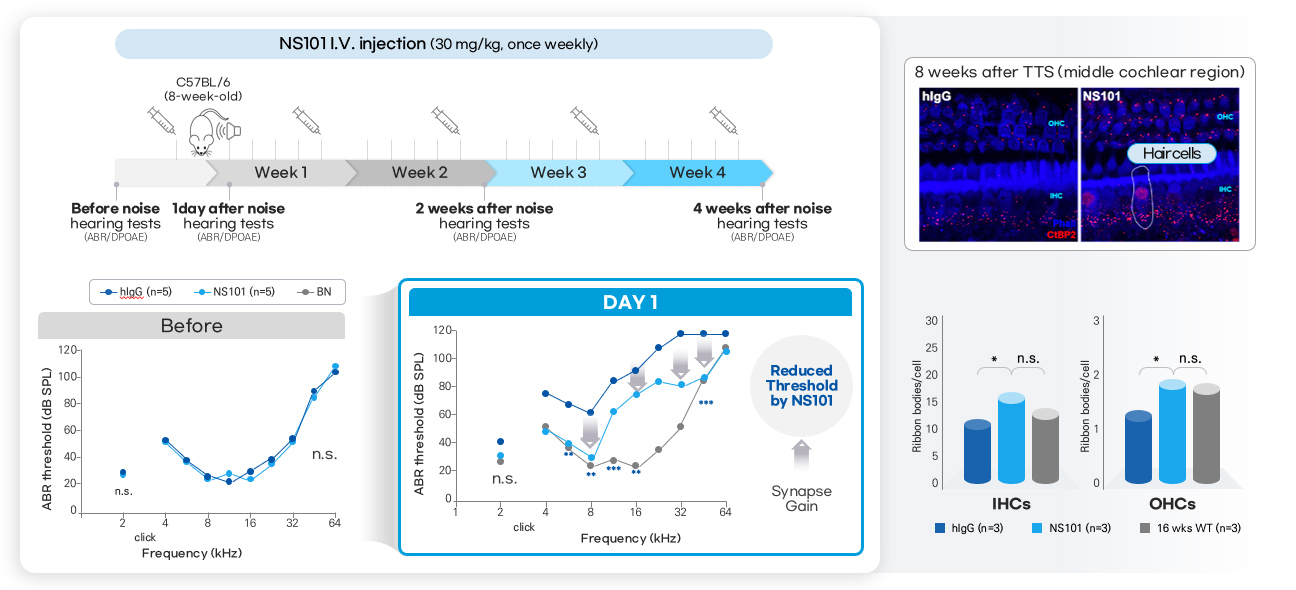
NS101 prevents post-noise decreases in cochlear ribbon synapses